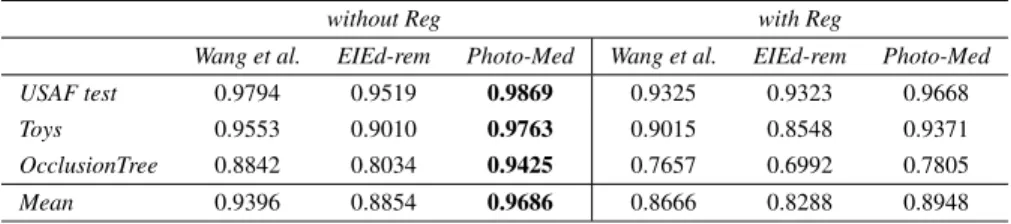
Depth and All in Focus Image Estimation in Synthetic Aperture Integral Imaging Under Partial Occlusions
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
The reduction of the uncertainty gives a measure of the ex- pected information that the evaluation of the evidence delivers to the decision process in a forensic case, and it
In order to achieve this goal, we report an empirical study that attempts to systematically measure the effects of two variability sources in the estimation of the number of
Government policy varies between nations and this guidance sets out the need for balanced decision-making about ways of working, and the ongoing safety considerations
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Jointly estimate this entry game with several outcome equations (fees/rates, credit limits) for bank accounts, credit cards and lines of credit. Use simulation methods to
In our sample, 2890 deals were issued by less reputable underwriters (i.e. a weighted syndication underwriting reputation share below the share of the 7 th largest underwriter
Two different types of simulations have been performed in order to, first, get knowledge about the isoplanatic area at the Teide Observatory, in both diurnal and nocturnal scenarios
The proposed reliability measure (the R-measure) analyses the shape of the focus measure function and estimates the likelihood of obtaining an accurate depth estimation without