Propagation Mechanism modeling in the Near-Region of Arbitrary Cross-Sectional Tunnels.
Texto completo
Figure
Documento similar
Thus, the main contributions of this paper are (i) a strategy to detect relevant behavioral changes based on a ranking mechanism in a given share of hosts, (ii) an approach to model
No obstante, como esta enfermedad afecta a cada persona de manera diferente, no todas las opciones de cuidado y tratamiento pueden ser apropiadas para cada individuo.. La forma
In this first report we describe data from the cross-sectional phase of the study, which aimed at evaluating: (i) the proportion of patients with controlled, partly controlled
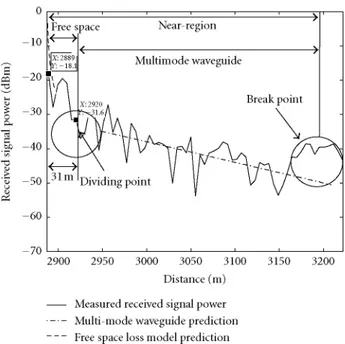
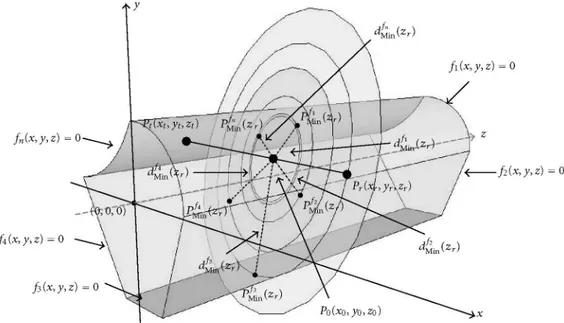
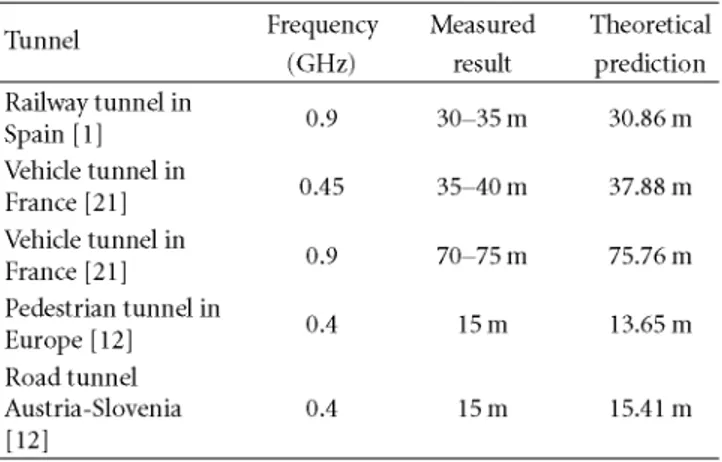
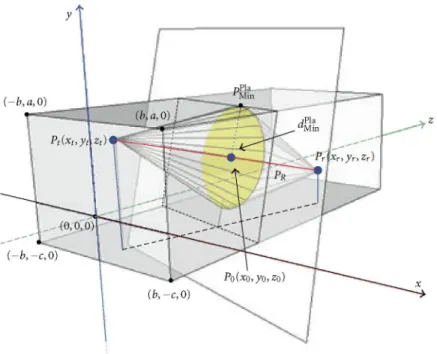
Comparing the previous results, it can be noticed that in the first and second zones of propagation, the deviation of the propagation loss from its main value is higher when
The characteristic morphology of the ZnO thin films is shown in the top-view FESEM image of Figure 3a, and a magnified cross- sectional image is shown in Figure 3b, which confirms
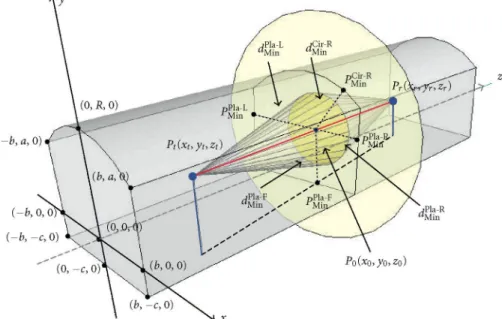
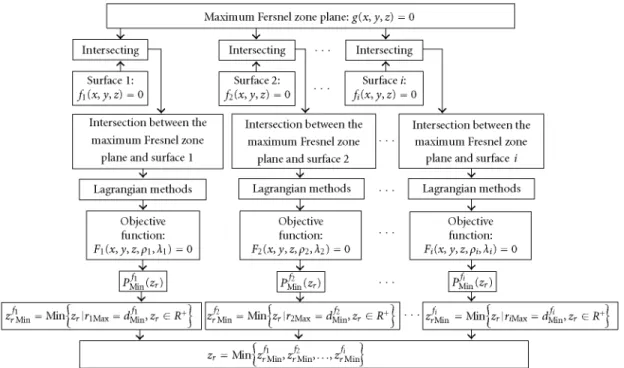
The main aim of this work is to develop a consistent theory to determine the self-gravitational potential at an arbitrary point of each component of a detached close binary system in
As part of the cross-sectional ESCARVAL objectives, by means of the analysis of the electronic medical records, this present study determined the clinical inertia in the diagnosis
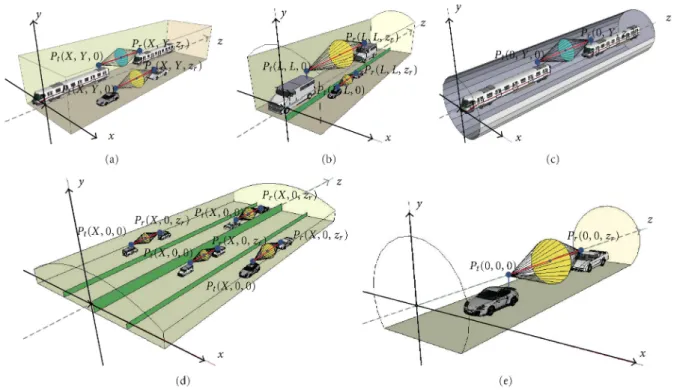
The principle behind this meth- od shown in Figure 1 is to create the desired channel model by positioning an arbitrary number of probe antennas in arbitrary positions within