Combinatorial antitumor effect of HDACs and the PI3K Akt mTOR pathway inhibition in a Pten deficient model of prostate cancer
Texto completo
Figure
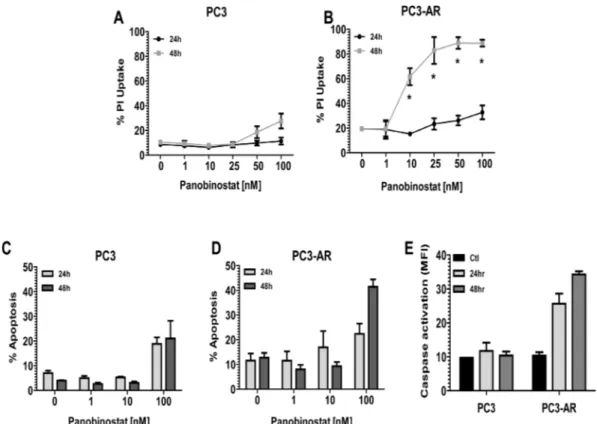
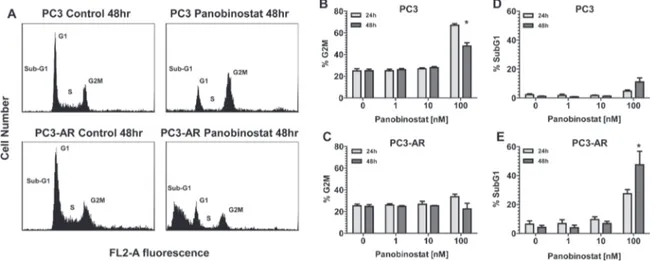
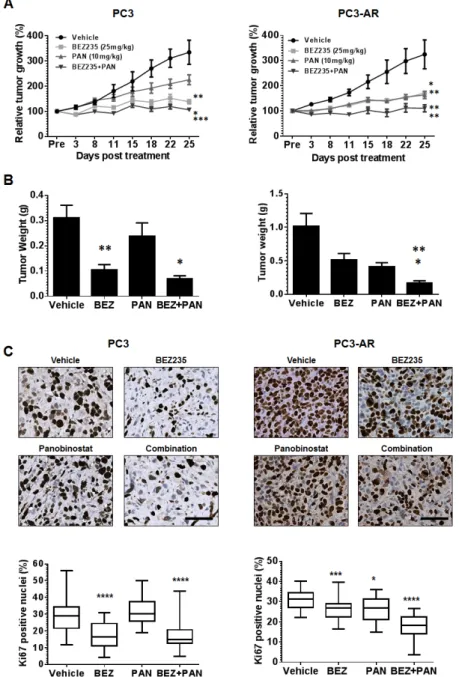
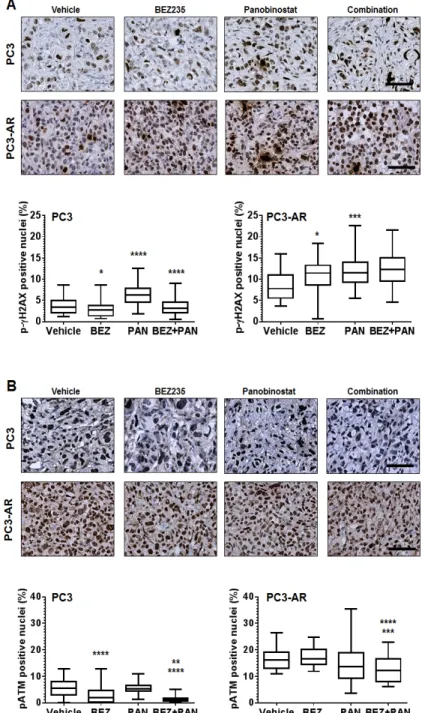
Documento similar
Cellular stress or inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway promote the translocation of FOXO factors to the cell nucleus, where their transcriptional functions can be executed..
It is thought that a defective or missing BRCA1 protein is unable to repair damaged DNA or fix mutations that occur in other genes, which is the main cause of its association
In the present work, we describe DYRK2 as a new kinase that regulates NOTCH1 pathway via phosphorylation, con- trolling its protein levels and activity in response to DNA
With the aim of determining which is the contribution of the content of carnosic acid and carnosol to the antitumor activity of the RE’s, and thus explain the different activities
the extrinsic and the intrinsic pathway. The intrinsic pathway integrates signals generated by a variety of stressors, including DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, loss
estradiol, beginning 6 h after the onset of pMCAO, par- tially recovered the activity of the PI3K/Akt/GSK3/β-cate- nin pathway, although this effect was more pronounced in the
The correlation of DisA with recombinational functions arose from three premises: (i) in the current model of DisA’s role as a DNA-damage checkpoint protein (See Figure 7), binding to
In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of platinum(II) complexes with thiosemi- carbazones derived from 2-formyl and 2-acetyl pyridine and con- taining