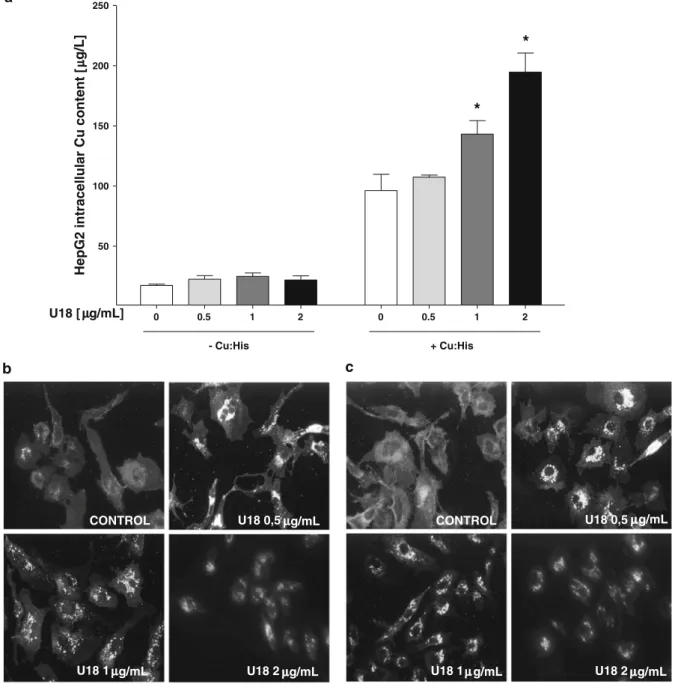
Increased copper levels in in vitro and in vivo models of Niemann Pick C disease
Texto completo
Figure


Documento similar
106, 257003 (2011)] measuring the dynamics of quasiparticle trapping in a superconducting atomic contact coupled to a Josephson junction.. With realistic parameters, the theory
2.- En la actualidad, se sabe que HNF1D promueve la acetilación de histonas en sus genes diana, aunque se desconoce si regula otras modificaciones de cromatina importantes para
Cell viability after shipment was > 80% in all cases, enabling evaluation of (1) adhesion to plastic flasks and hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate osteoconductive
This technique efficiently allowed the release of Nrf2 for its nuclear translocation: higher levels of nuclear Nrf2 were detected under basal conditions and after 4 and 8 hours of
We find that hepatic GRK2 protein levels are upregulated in different mouse models of steatosis and, conversely, we demonstrate that the development of NAFLD
competed against other partners, fluorescent protein reassembly will be different and thus, also changes in fluorescence signal could be detected (Figure 2.6). Moreover, we have
In addition, given the widespread use of prescription benzodiazepines in society, and their diversion to the illicit drug market, the increase in new benzodiazepines might also
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the