The numerical analysis of fault-induced mine water inrush using the extended finite element method and fracture mechanics
Texto completo
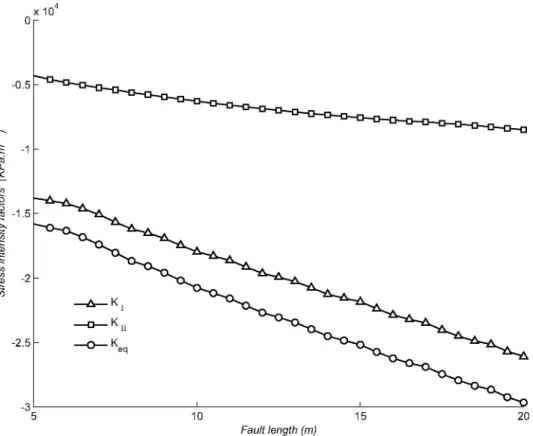
Figure



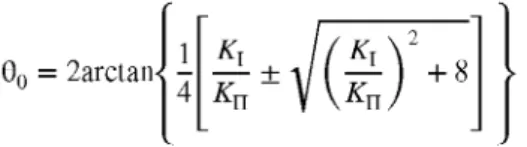
Documento similar
The proposed strategy combines the active method to improve the vector control strategy in order to limit fault in current at low voltage dips and the passive method
On the other hand, with the use of CROWBAR circuit protection it is observed that during the grid fault the rotor current and the active power almost zero due to separating of
The characteristics of this occurrence differ from those of fluid-deposited vein-type graphite mineralization in that: (1) graphite flakes are oriented parallel to the vein walls;
The above analysis leads to an experimental scenario characterized by precise mea-.. Figure 4: The allowed region of Soffer determined from the experimental data at 4GeV 2 ,
We remark that we do not take advantage of fast Fourier transforms for linear terms, because the corresponding matrices are constant at each time step as we will see below..
An initial numerical study of the transducer was done using the finite element method (FEM) software COMSOL Multiphysics®. The aim of this design was to obtain a very resonant system,
Flt2sch reads a fault diagnostic file ( .dia ) created by the HILO fault simulator and produces Schedit command files (with a .flt extension), one for each schematic file,
In this paper we analyze a finite element method applied to a continuous downscaling data assimilation algorithm for the numerical approximation of the two and three dimensional