Brain-wide slowing of spontaneous alpha rhythms in mild cognitive impairment
Texto completo
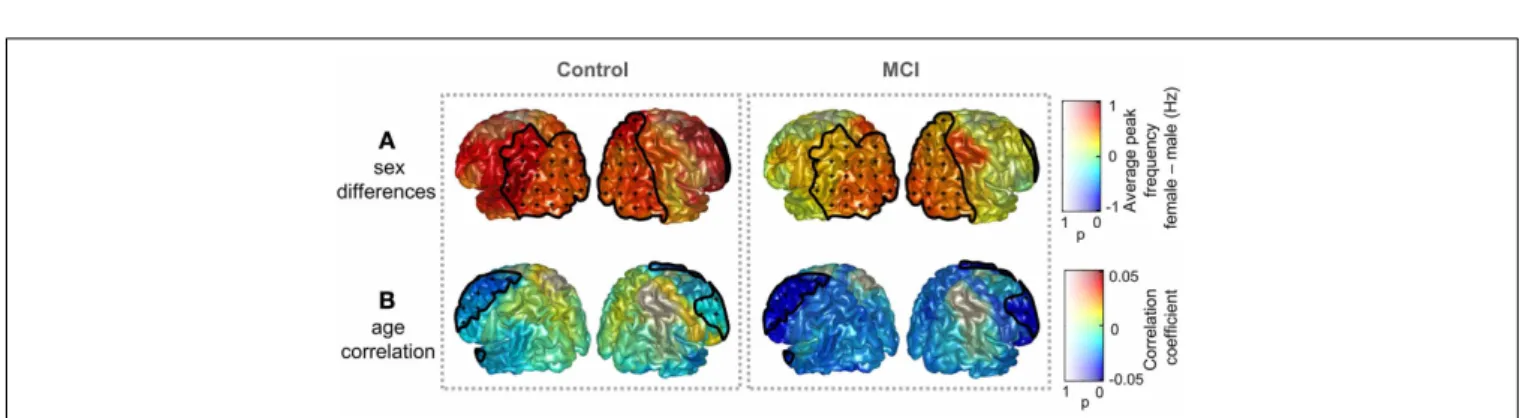
Figure


Documento similar
"Tis solike flatt'ry, which I hate.. BY EDWARD MOORE.. FABLES. Cried, Sure there never was in nat ure So elegant, so line a
Table VII shows the results of the five tests assessing visual object and visuospatial skills. The cognitively preserved group did not show statistically significant differences
picture in Figure 6, are a Focal Plane Mask (FPM) with a grid of pinholes, and a Natural Guide Star Assembly with up to Figure 5 Left: Evacuated Double Pane Entrance Window;
We found a higher amplitude of regional spontaneous activity in bilinguals compared to 236. monolinguals in the thalamus bilaterally (Fig 2; Table
de se convertir en chaux par la calcination- L a formation de ces pierres nous paroît due, en grande partie , au détritus des coquillages : Tidentité des
For adults with normal cognition or mild cognitive impairment, are physical activity interventions more effective than usual care or no intervention in reducing the risk of
Although both spike train and total current cross-covariance functions are small, the asynchronous state is characterized by finite values of cross-covariances between the
MCI participants performed at the same level as the control group in discrimination tasks, emotional labelling, prosody comprehension tasks, and immediate facial emotional memory