Characteristic molecular properties of one electron double quantum rings under magnetic fields
Texto completo
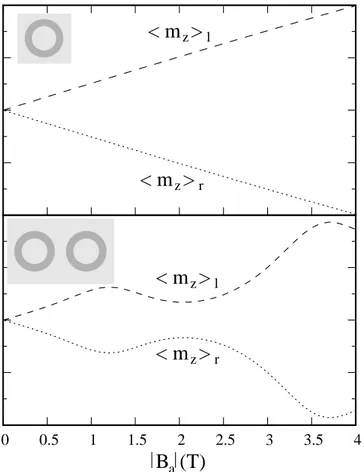
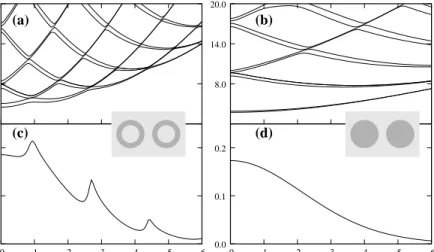
Figure



Documento similar
properties of an epitaxial monolayer of graphene grown on Ru(0001) (gr./Ru), and the adsorption of the molecular electron acceptor 7,7 0 ,8,8 0 -tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) on
The axial magnetic effect describes the generation of an energy current parallel to an axial magnetic field B 5 (i.e., a magnetic field coupling with opposite signs to the left
At fixed temperatures, between 1.6 and 6 K, the frequency dependence of the AC susceptibility also shows slow magnetic relaxation under applied static DC fields, (Figure
van der Meulen, J. Single-photon emission by semiconductor quantum rings in a photonic crystal. Controlling the properties of single photon emitters via the purcell effect.
Previous experimental and simulation studies of superparamagnetic colloids in a strong external field have systematically shown a nonequilibrium aggregation process in which chains
The scope of this Thesis is the investigation of the optical properties of two systems based on semiconductor nanostructures: InAs/GaAs quantum rings embedded in photonic
In this context, one advantage of using the multiplicity instead of the Hilbert-Samuel function (the invariant used by Hironaka in [14]) is that, at least when the
In the second scenario (bottom panel), the Auger electron is ejected later, when the molecule has begun to dissociate, and transfers the recoil momentum to only one of the two